
Rhinoplasty or rhinoplasty is a branch of plastic surgery that specializes in correcting congenital or acquired deformities and restoring individual nasal segments or the entire organ.
Rhinoplasty can increase or decrease the size of the nose, change its shape, and eliminate breathing problems. The aesthetic goal of rhinoplasty is the harmony of facial features by correcting nasal defects. This type of surgery is usually performed at the age of 18-21 years, as there is a physiological growth of bone and cartilage tissue in the meantime.
The task of rhinoplasty is to restore the shape and function of the nose that has been damaged due to injury or during embryogenesis. Rhinoplasty is a series of different operations that are discussed in more detail below.
Israeli clinics give excellent results, medical care meets the expectations of patients.
Open or closed access can be used during Israeli rhinoplasty, depending on the purpose of the surgery. In a closed rhinoplasty, an incision is made in the cavity, and the skin is detached from the skeleton (cartilage and nasal bones). This method is used to change the shape, remove cartilage and excess bones, and so on. are applied. If high-volume surgery is planned, open rhinoplasty of the nose is prescribed when it is incised in the columella (the vertical skin fold that separates the nostrils).
Nasal correction is divided into primary and secondary. Revision or secondary plastic surgery is performed to correct any defects remaining after the primary surgery.
In recent years, fillers have been actively used in rhinoplasty to correct minor imperfections in the nose: to change the shape of the wings, to restore symmetry, to round the tip of the nose, and so on.
Rhinoplasty surgery in Israel: design and construction

At Israeli clinics, a plastic surgeon first visits the patient, examines the shape of the nose, the condition of the tissues, and diagnoses nasal breathing disorders. For best cosmetic results, photos are taken and computer modeling of the nose is done. The patient is also consulted by an otolaryngologist. In case of pronounced defects, if the nasal breathing is disturbed, rhinoplasty is performed with the help of an otolaryngologist and a plastic surgeon.
General anesthesia in combination with local infiltration anesthesia is usually used during surgery. The duration of rhinoplasty depends on the complexity and takes 1-2 hours or more. For a more aesthetically pleasing size and shape of the nose, the surgeon replaces the skeletal and cartilage skeletons. Properly performed rhinoplasty in Israel and the lack of complications - and scars after surgery won’t actually be visible.
Recovery period after nasal correction
After surgery, tampons are placed in the nasal passages and removed after 2-3 days. To fix the new shape, a special plaster or colloidal sticker should be applied for 5-7 days (if the plastic touched the cartilaginous part of the nose) or for twelve to fourteen days (if the bony part).
Swelling can cause nasal breathing in the first few weeks. The bruises and swelling disappear within ten to fourteen days. Wearing glasses for one and a half months after nasal correction is not recommended. Full recovery takes six to eight months, at which point the final result of the surgery will be visible. Smoking and taking certain medications can slow down your recovery.
Rhinoplasty in Israel: removal of the nasal congestion
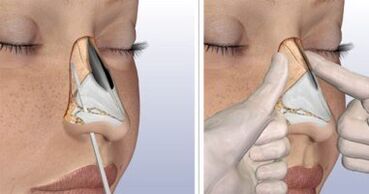
This operation is multi-step. During its implementation, the osteocartilaginous protrusion of the back of the nose ceases. Humped back can be caused by trauma or hereditary factors.
If the nasal hump is small, local anesthesia may be used, if large - general. The duration of the surgery is 1-2 hours.
First, the surgeon cuts and removes the skin from the bone cartilage base of the nose - the stage of skeletalization. The cartilage is then excised and the cartilaginous segment of the septum is gradually removed, starting from the smallest volume. The bone component of the nasal bone is then excised.
After removal of the hump, the skeleton takes the form of a truncated pyramid. An osteotomy is performed to join the nasal bones and remove the wide platform. The surgeon cuts the bone tissue from the side slopes and brings them closer to the upper segments. To eliminate the unevenness, the patient uses contour plastic surgery with his own cartilage or various implants. At the end of the nasal correction, cotton swabs are placed in the nasal passages and a plaster bandage is applied to secure the new position of the tissues. The plaster is removed after eight to ten days.
Bleeding and swelling in the nasal area persist for a few weeks after the nasal bulge is removed. As the edema decreases, nasal breathing recovers. The outcome of the surgery can be assessed after six months, when the tissues are completely recovered.
Nasal septoplasty in Israel
This surgery is used to correct the nasal septum while preserving the skeletal and cartilage skeleton. This type of plastic makes it possible to achieve an aesthetic result and eliminate breathing difficulties.
The nasal septum is a thin vertical plate of bone and cartilage that deforms easily, leading to impaired respiratory function and aesthetic deterioration. The causes can be injuries, childhood English disease, hereditary predisposition.
Contraindications include:
- severe pathologies of the internal organs;
- oncology;
- infectious diseases;
- blood clotting problems;
- diabetes.
Indications for nasal septoplasty:
- allergic pathologies (itching, runny nose, etc. );
- difficulty and lack of nasal breathing;
- chronic and acute diseases of the paranasal sinuses (frontitis, etmoiditis, sinusitis);
- vasomotor rhinitis and frequent epistaxis;
- snoring due to nasal breathing, etc.
In case of exacerbation, the septoplasty is performed two weeks after its termination. The indication for Israeli surgery is determined by the otolaryngologist based on the medical history and diagnosis (rhinoscopy). Before the operation, laboratory tests, ECG and lung X-ray are performed.
Infiltration anesthesia (injected into the nasal septum by injection), topical anesthesia (anesthesia-soaked turundas are injected into the nasal passages) and general anesthesia can be used as analgesics.
In Israeli septoplasty, the surgeon makes an incision inside the nose or endonasally, resulting in no visible postoperative scar. It peels off the mucous membranes on both sides of the nasal septum, highlighting and removing the curved portions of the bone structures and the rectangular cartilage of the hedge. After nasal correction, sutures are applied and tamponing is performed with a finger or gauze wipe. A strap-like bandage is placed on the nose.
In addition, in Israel, septoplasty is performed with endoscopic access. An endoscope with fiber optics is inserted into the nasal cavity, allowing hard-to-reach sections to be viewed on the monitor and performed as accurately as possible. This type of septoplasty causes minimal damage to the cartilage and tissues in the nose, reducing the healing period.
In addition, laser septoplasty is used in Israeli clinics to prevent bleeding and edema, as the laser "closes" the blood vessels by cutting the tissue. It also provides an antiseptic effect.
The duration of septoplasty is determined by the degree of curvature of the septum, and surgery can last from thirty minutes to one and a half hours.
This type of rhinoplasty is quite easily tolerated. The patient is in the hospital until the nasal swab is removed. Ten to fourteen days is enough to restore your ability to work, and full rehabilitation takes about a month.
Rhinoplasty in Israel: Convergence of the Nasal Bones
Israeli osteotomy (bone repositioning, bone convergence) can be a stand-alone surgery that corrects the shape of the nose, or one step in removing the nasal bulge. Thanks to this type of plastic surgery, the surgeon achieves the ideal ratio of nose to face, reducing the side bones of the nasal saddle.
During osteotomy, it brings together the walls of the bone pyramid, and then the cartilage attached to the bones moves. The skin usually adapts without difficulty to the altered contours of the back of the nose.
Osteotomy takes a few minutes for the entire duration of rhinoplasty. Upon completion of the correction, the nose is sealed with surgical plaster and bandaged to retain its shape and protect it from injury.
Within 2 weeks, the hematomas and edema disappear. Eventually, new contours emerge within a year.
Rhinoplasty in Israel: Supporting the tip of the nose
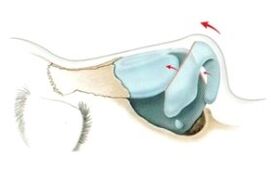
The support of the nasal tip is ensured by a stable, strong and correct arrangement of the cartilage. They are usually slightly above or below the line running at the back of the nose.
Insufficient support is caused by the undesirable consequences of rhinoplasty (if adequate support is not provided) or age-related tissue ptosis (weakening of the ligaments supporting the cartilage).
For support, the entire outer nose is proportionally and correctly formed. The norm is the nasolabial angle (formed by the upper lip and the columella) - 90-120 °.
During Israeli rhinoplasty, the tip of the nose can be raised seven to eight millimeters above the back profile line. The skin of the mountain is difficult to adapt to change because it is less elastic and thicker.
Transplanted cartilage grafts - "supplies" - can be used to restore the support. The surgeon places and fixes such cartilage between the side cartilages and then cuts it to the desired size.
In addition, the graft can be placed perpendicular to the support on the cartilage. This option is used when the cartilage of the tip of the nose is damaged and is not used for self-support. The ideal source of graft is cartilage from the nasal septum.
If a graft cannot be obtained from the apex, the cartilage can also be removed from the wing. However, they are not considered strong enough to hold pressure and shape. Therefore, ear cartilage is often associated with a strong and thin bony nasal septum. A portion of the bone is glued to a cartilage graft.
Rhinoplasty in Israel: short for nose
Nasal shortening is a plastic surgery that reduces the length of the outer nose. Most often, the length of the cartilage of the septum decreases, less frequently the side wall of the nose, which is formed by large alar, triangular cartilage and bones.
Various methods are used to estimate the length of the nose. The most common method is to measure the distance between the tip of the nose and the saddle. Another method involves determining the magnitude of the nasolabial angle.
As you age, the cartilage-holding ligaments weaken, the tip of your nose falls off, and visually increases in length. Because of this, in patients, patients shorten the length of the nose less than in young people.
Types of nose shortening surgeries in Israel
In the case of a long nose, the cartilaginous and bony sections of the nose, the transverse and longitudinal directions of the triangular and mandibular cartilages, and the cartilaginous part of the septum are usually elongated evenly. As a result, either surgeries to shorten the lateral cartilage wall of the nose or resection of the distal septum are performed.
In the second option, partial resection is performed under infiltration anesthesia. The surgeon performs 2 parallel transfection incisions through which the cartilaginous septum is resected from the mucosa and excised skin strips in the columella area. The incisions are then sewn with catgut threads. As a result, the nose shortens and the nasolabial angle increases.
Another method is to increase the nasolabial angle by placing silicone or cartilage liners in front of the maxillary spine.
Rhinoplasty in Israel: nasal tip correction
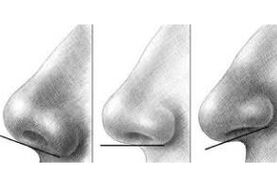
This type of rhinoplasty can be performed in Israel in several ways. The surgery is performed on the terminal section of the outer nose: its shape is improved by removing deforming or excessive parts of the cartilage tissue and a new position is fixed.
Correction of the nasal tip is a complex part of rhinoplasty, the task of which is to restore harmonious anatomical properties without disturbing the supporting structures of the organ.
Due to the variety of nasal tip correction options, an individual rhinoplasty plan is developed in Israel that takes into account the firmness and shape of the cartilage, the thickness of the skin, the width and length of the nose, the nasolabial angle, and the anatomy of the nose. vault angles, back contour and patient preferences.
To narrow the tip of the nose, the surgeon cuts out the segments of the alar cartilage and partially removes the adipose tissue. A variant can be used in which the domes are cut and seams are applied, narrowing or joining them.
Rhinoplasty in Israel: Relocating a broken nose
This nasal correction operation involves bringing the displaced bone pieces to a normal position. The optimal time for this plastic surgery is the first hour after fracture, until the development of soft tissue edema, or the next 3-7 days, when the edematous condition decreases. Hardening of the skin occurs 10 days after the injury, repositioning is no longer possible.
Forty percent of all facial injuries are nasal fractures caused by sports injuries, street and home fights, traffic accidents, and falls. Such a fracture can be closed and open, with no displacement and displacement of bone fragments. Symptoms of fracture include deformity of the outer nose, swelling, pain, mucous discharge, bleeding, wounds, abrasions, nasal bleeding due to rupture of the mucosa. In addition, the sense of smell and nasal breathing is impaired.
For diagnostic purposes, the patient is interviewed in Israel, and external and endonasal examinations, endoscopic examinations, and radiographs of the nasal bones may be performed.
A fairly common consequence of a bone fracture is curvature of the nasal septum, accompanied by recurrent sinusitis, rhinitis, and nasal breathing. Curvature correction can only be performed surgically.
A further complication may be a hematoma of the nasal septum under the mucous membranes, which narrows the lumen of the nasal passages and makes it difficult to breathe. Maybe its purulence and subsequent cartilage destruction. Therefore, high quality and prompt medical care for nasal fractures is extremely important.
A cold (ice or cold compress) can be used as a first step to reduce swelling and pain and stop bleeding.
At the Israeli clinic, plastic surgeons perform repositioning of bone fractures. For the first 6-7 days, repositioning is performed manually under local anesthesia to allow the bones to merge properly in the future. Tight tamponing of the cavities is performed with turundas to press and support the nasal skeleton. A bandage is used on the outside.
Due to further trauma, self-reduction is strictly prohibited. After relief of swelling, the aesthetic and respiratory function of the nose is assessed. Bone fractures cause deformity and lateral displacement of the bone cartilage of the nose, narrowing of the nasal passages, curvature of the septum, and so on.
If the nasal bones do not grow together properly, patients are often forced to undergo rhinoplasty afterwards. In order to restore damaged breathing, the deviated septum is corrected - rhinoseptoplasty is performed.
Rhinoplasty in Israel: Correction of the wings of the nose
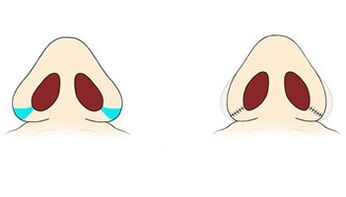
These types of operations are performed to change the width, thickness, and symmetry in the event of pronounced aesthetic defects and deformations. Different methods are used depending on the violations. For repair, the tissues surrounding the defect are mobilized or a cartilage or skin graft is moved.
Correction of the wings of the nose can be independent surgery or the last stage of rhinoplasty in Israel.
The defects of the nasal wings are acquired and congenital, complete or partial. The causes are the consequences of nasal correction or removal of tumors, trauma, burns and illness.
Most operations to repair the nasal wings are performed under local infiltration anesthesia. If there are extensive defects, intravenous anesthesia is used.
Sometimes tip augmentation is used to correct the nasal wings. In this case, this operation completes the rhinoplasty. If aesthetic defects occur, the correction is performed at the main stage of the surgery.
If the distance between the wings of the nose is to be reduced, incisions should be made at the bottom of the wings from the vestibule and along the contour. Skin and mucosal segments are excised, hemostasis is performed, and sutures are applied. The scars are located in the folds of the nasal wing and in the natural nasolabial folds, making them virtually invisible.
If the support of the nasal wings needs to be restored (in case of retraction or injury), areas of adjacent tissues are moved, specially modeled by transplanting a skin flap or own cartilage from the earlobe or nasal septum.
The rehabilitation period can last for five days, seven or more in the case of cartilage reconstruction.
Rhinoplasty in Israel: complete nasal correction
This type of rhinoplasty in Israel involves complex rhinoplasty performed in the structural segments of the outer nose and in the thickness of the tissues of the organ. They can reduce the length of the nose, change its shape, remove the hump, narrow the width of the back, adjust the tip. Together with the plastic, they restore respiratory function and the normal architecture of the cavity.
This operation is most often performed after injuries.
In most cases, the correction is performed with a closed (endonasal) approach, excluding external skin incisions. Superficial manipulations can be performed under local anesthesia and intravenous sedation, and surgeries on deep structures require general anesthesia. This nasal correction is possible in the 18-40 age group.
Rhinoplasty in Israel can be combined with the following plastic surgeries: blepharoplasty, facial surgery, chin and lip surgery, liposuction, breast augmentation, etc.
Prior to surgery, the anatomical structure of the nose is carefully analyzed and its future shape is modeled on a computer. In case of violation of nasal breathing, the nasal cavity is examined and radiography or tomography is performed.
Modern rhinoplasty in Israel uses cost-effective techniques that provide excellent results and minimize the likelihood of complications.






















